Pub/Sub messaging platform for serverless
Efficiently design, quickly ship, and seamlessly scale critical realtime functionality
Simple, scalable and serverless

About Ably
Ably is a fully-managed pub/sub messaging platform with a suite of integrated services for building complete realtime applications that seamlessly integrate with AWS Lambda. It enables you to communicate between your serverless functions and user devices over persistent connections across our global edge network. Built with AWS Lambda and the broader AWS ecosystem in mind.
Ably integrates with a wide range of Amazon products (EventBridge, SNS, SQS, Kinesis), and is frequently used as a full-featured replacement for Amazon API Gateway WebSockets. With Ably, you can be up and running in minutes, delivering realtime capabilities you can trust to a global audience at any scale.
A better API Gateway Websockets
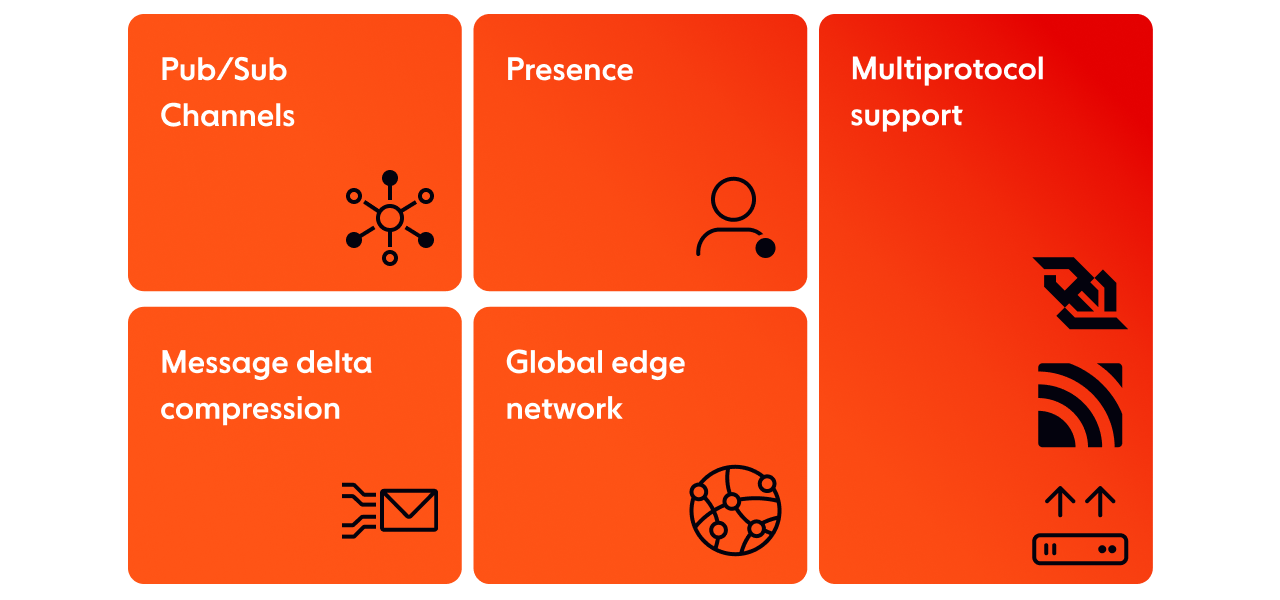
A fully integrated suite of realtime features:
Pub/Sub Channels: Publish to a limitless number of subscribers with access to message history.
Presence: Keep track of when devices or users are online.
Multiprotocol: Native support for WebSocket, MQTT, SSE, and others.
Message delta compression for bandwidth-efficient streaming.
Global edge network ensures low latencies for client devices.
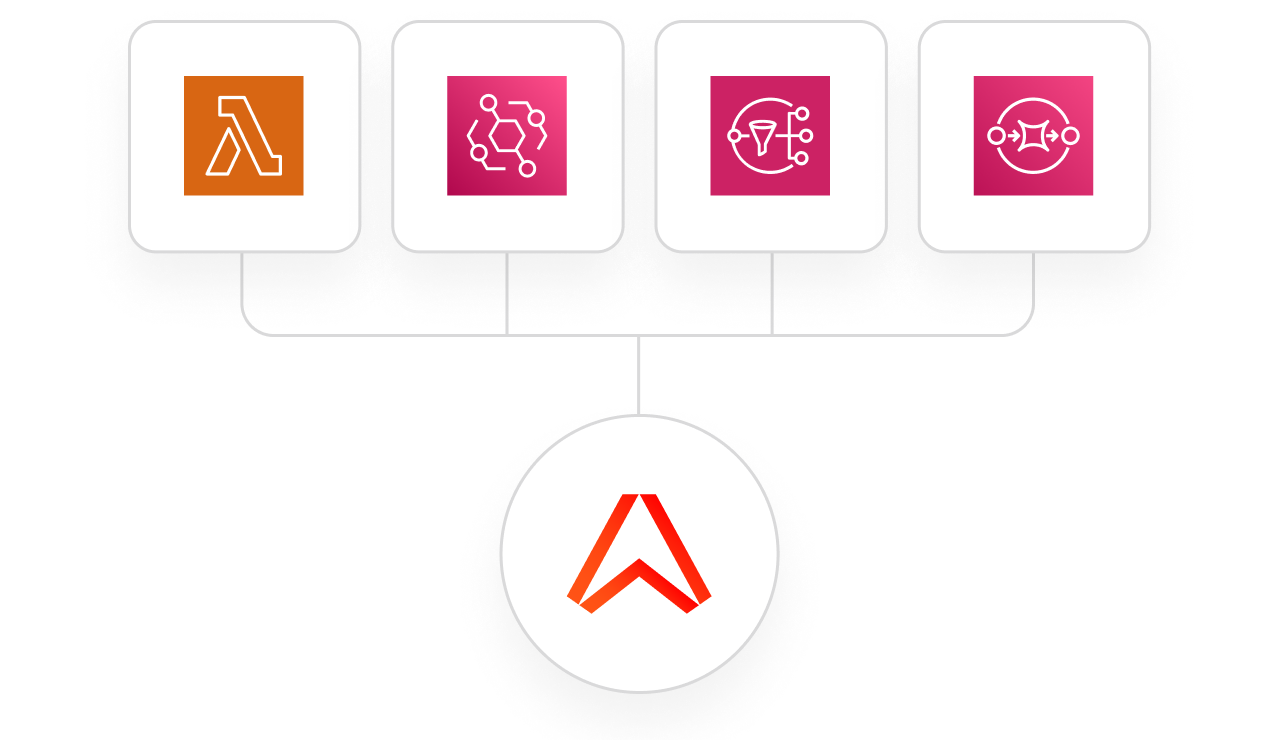
Quickly and seamlessly integrate with your AWS stack
Deploy best-in-class tooling across your entire stack, and build event-driven apps using the ecosystems you’re already invested in. Integrate natively with AWS Lambda, and with the wider AWS ecosystem (e.g., Amazon EventBridge, Amazon SNS, Amazon SQS, Amazon Kinesis).
Built with serverless in mind, Ably enables you to use Lambda functions to process message data in real time, and synchronize state back to your end-user devices simply, with support for every popular platform using our 25+ native SDKs.
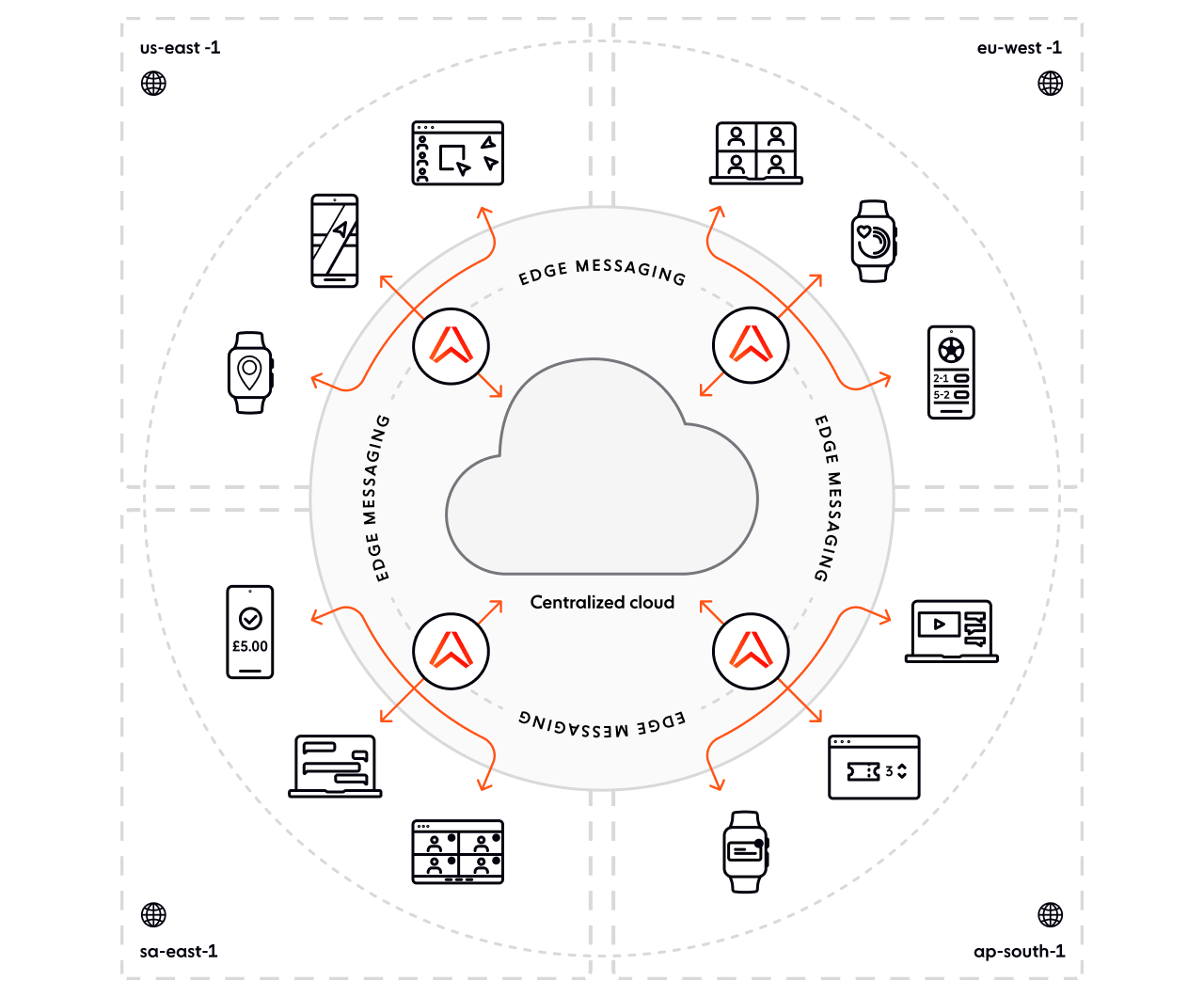
All the benefits of serverless, with our pub/sub edge network
Reduce engineering complexity of solving realtime problems, streamline DevOps, and increase development velocity by using the right tool for the right job at the right capacity:
Focus on realtime features with our simple APIs and SDKs instead of on complex event-driven engineering.
Eliminate DevOps with a fully managed cloud-native edge solution.
Ship realtime experiences quickly with a complete suite of services.
Minimize cost by paying for only what you use with a ready to scale platform.
Internet scale from day one with a platform that effortlessly delivers billions of messages each day.
Deploy globally as a default over our global edge network with fault tolerant infrastructure, high availability, and median response latencies below 50 ms.
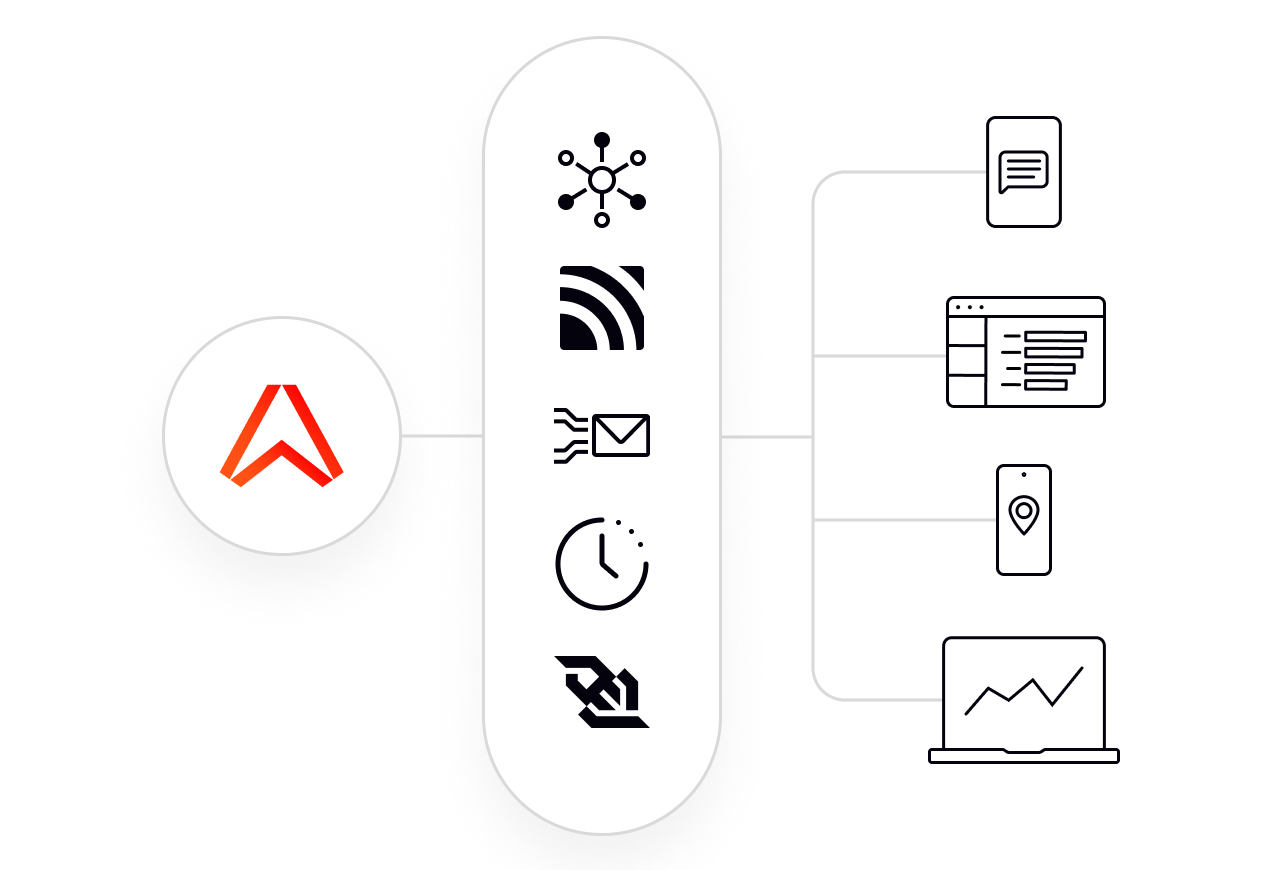
Simplify synchronization between your apps and serverless architectures
Every stateful channel on the Ably network provides integrity guarantees and rich functionality to enable:
Pub/Sub with exactly-once ordered message delivery
Message delta compression for efficient state synchronization
Keep the last message on channels for long term state storage
Stream over any protocol including WebSockets, MQTT, SSE, etc.
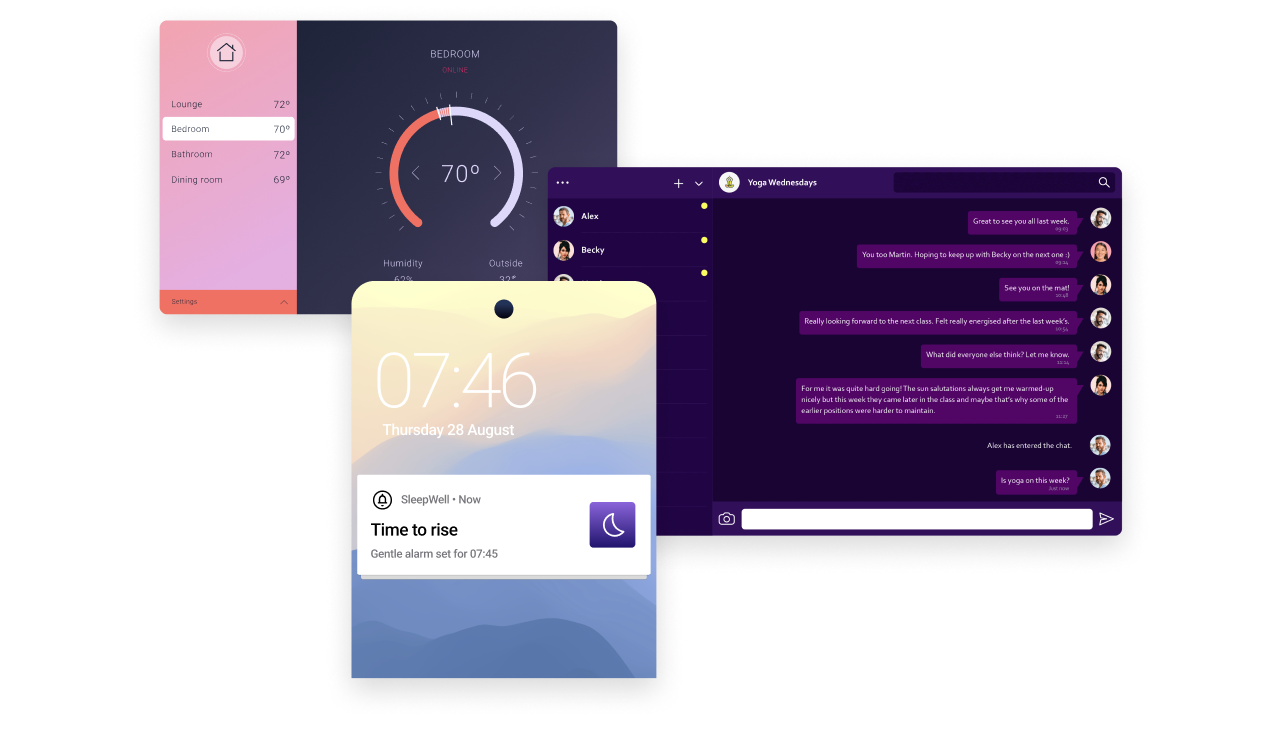
What you can build with Ably
Ably delivers billions of realtime messages everyday to more than 50 million end-users across web, mobile, and IoT platforms.
