- Topics
- /
- Protocols
- &Development platforms & operating systems
- /
- WebSockets and tvOS apps: client-side engineering aspects you need to consider
WebSockets and tvOS apps: client-side engineering aspects you need to consider

At a global level, there is an ever-increasing appetite for data delivered in real time, with WebSockets being probably the most popular transport protocol for such use cases. Before WebSockets came along, the “realtime” web existed, but it was difficult to achieve, typically slower, and was delivered by hacking existing web technologies which were not designed for realtime applications. The WebSocket protocol paved the way to a truly realtime web.
tvOS is a dedicated platform for Apple TV that is heavily inspired by iOS. Initially known as Apple TV Software, tvOS was renamed and launched in 2015 when Apple introduced the 4th generation Apple TV, with support for third-party applications.
tvOS leverages the unified standard library frameworks that are part of the Apple developer ecosystem. The WebSocket protocol is available as part of the URLSessionWebSocketTask class available within the Foundation framework. For low-level WebSocket protocol access, you can also use the Network framework, which provides fine-grained control on WebSocket protocol connection and packet transport, via the NWProtocolWebSocket class. These classes are available for tvOS in Swift (and Objective-C, but only for the former).
Since demand for realtime data is growing steadily, and with tvOS being a popular operating system, I think it’s worth looking at some of the many challenges of implementing a dependable client-side WebSocket solution for tvOS apps.
State of play — a brief overview
Rarely is a basic or raw WebSocket implementation enough for the needs of a realtime app that services an unknown (but potentially very high) number of users. Most of the time, you need to think about extending the capabilities of your tvOS client-side WebSocket implementation.
For this purpose, you could use open-source libraries like SocketRocket or Starscream, which include some additional functionality, such as TLS or proxy support. With Starscream, this is how you connect to a WebSocket server:
var request = URLRequest(url: URL(string: "http://localhost:8080")!)
request.timeoutInterval = 5
socket = WebSocket(request: request)
socket.delegate = self
socket.connect()And this is how you monitor connection events and receive data over WebSockets:
func didReceive(event: WebSocketEvent, client: WebSocket) {
switch event {
case .connected(let headers):
isConnected = true
print("websocket is connected: \(headers)")
case .disconnected(let reason, let code):
isConnected = false
print("websocket is disconnected: \(reason) with code: \(code)")
case .text(let string):
print("Received text: \(string)")
case .binary(let data):
print("Received data: \(data.count)")
case .error(let error):
isConnected = false
handleError(error)
}
}However, while it’s true that libraries like SocketRocket or Starscream offer some benefits, they are essentially just wrappers around a WebSocket client; they provide no functionality on top.
To get the most out of WebSockets, a protocol that’s built on top is often used, which enables richer functionality, such as pub/sub. You could choose to develop your own WebSocket-based protocol that is tailored specifically to your needs. However, that is a very complex and time-consuming undertaking. Most of the time, you are better off using an established WebSocket-based solution that is well prepared to handle an entire set of engineering complexities.
Here at Ably, we have a protocol for pub/sub that is used on top of WebSockets. It allows you to communicate over WebSockets by using a higher-level set of capabilities. To demonstrate how simple it is, here’s an example of how data is published to Ably:
let ably = ARTRealtime(key: "ABLY_API_KEY")
let channel = ably.channels.get("test")
// Publish a message to the test channel
channel.publish("greeting", data: "hello")And here’s how clients connect to Ably to consume data:
let ably = ARTRealtime(key: "ABLY_API_KEY")
let channel = ably.channels.get("test")
// Subscribe to messages on channel
channel.subscribe("greeting") { message in
print("\(message.data)")
}As you can see from the code snippets above, although the communication is done over WebSockets, the underlying WebSocket protocol is ‘’hidden’’ from developers.
You can decide to use any WebSocket-based protocol that supports tvOS. Regardless of your choice, though, you need to consider the entire spectrum of challenges you’ll face when it comes to WebSockets.
WebSockets and tvOS: what you need to consider
Before we get started, I must emphasize that this article only focuses on the client-side challenges of building a dependable WebSocket-based solution for tvOS apps. I assume you have already decided what solution you want to use on the server-side. If you haven’t yet, you can go with an open-source library like Socket.IO, or a cloud-based solution like Ably.
It’s also worth mentioning that I’ve written this article based on the extensive collective knowledge that the Ably team possesses about the challenges of realtime communication via WebSockets.
I’m now going to dive into the key things you need to think about, such as authentication, network compatibility, or handling reconnections with continuity. Your client-side WebSocket implementation must be equipped to efficiently handle all these complexities if you are to build a reliable system.
Do you actually need WebSockets?
WebSocket is the most popular and portable realtime protocol. It provides full-duplex communication over a single TCP connection. WebSockets are a great choice for many use cases, such as financial tickers, chat solutions, or location-based apps, to name just a few. But it’s not the only available option. Before jumping on the WebSocket bandwagon, you should look at the existing alternatives, to make sure they are not a better fit for your use case.
For example, MQTT, which also supports bidirectional communication, is the go-to protocol for IoT devices with limited battery life, and for networks with expensive or low bandwidth, unpredictable stability, or high latency. Another example is Server-Sent Events, a lightweight protocol from both an implementation and usage standpoint. It’s a superior alternative for most browser-based scenarios where unidirectional communication is enough, such as users subscribing to a basic news feed.
WebSockets, MQTT, and SSE are all TCP-based protocols. TCP is designed to be a reliable transport layer protocol, which provides message delivery and ordering guarantees. This is great for many realtime use cases. But for other use cases, a lightweight, speedier protocol is a better option. For example, if your purpose is to stream video data, you’re better off using UDP as your transport layer protocol.
Even if WebSocket is a good choice for your needs, depending on the complexity of your architecture and what you are trying to achieve with your system, you might want to have the flexibility of using multiple protocols, one for each specific use case.
Ably and protocol interoperability
Authentication
Generally, it’s a good idea to only allow authenticated users to use a WebSocket connection. However, a raw WebSocket request has no header, so you’re unable to provide authentication in the way you might with an HTTP request. That’s why you need to use another component or service for authentication.
A client-side WebSocket library might be an option, but be careful when selecting one, as not all of them provide authentication mechanisms (or if they do, they can be quite limited). Alternatively, you can build your own authentication service. Most of the time, though, you are better off using a mature, feature-rich solution, such as a realtime messaging platform, that handles not only authentication, but an entire set of engineering complexities related to streaming data over WebSockets.
Let’s now look at the most common authentication mechanisms you can use over WebSockets. The first one, basic authentication, is the simplest option available (and also the least secure) and it involves the use of API keys. The credentials are usually passed as a query parameter in a URL, which looks something like this:
wss://realtime.ably.com/?key=MY_API_KEY&format=json&heartbeats=true&v=1.1&lib=js-web-1.2.1
From a security perspective, it’s recommended to only use basic authentication server-side, because exposing an API key to multiple clients is highly insecure. In theory, if you use ephemeral API keys that expire after a given amount of time on the client-side, you minimize the risk of them being compromised. However, in practice, a URL containing an ephemeral API key would be broken as soon as the key expires. In addition, request logging services would capture the API key in server logs. Therefore, you would have to open a new WebSocket connection each time the API key is refreshed. This is not a scalable approach.
Token-based authentication is another widely-used authentication mechanism. One of the most popular methods of token-based authentication is called JSON Web Token (JWT). It’s an open and flexible format that has become an industry standard. At a basic level, JWTs work as illustrated in this diagram:
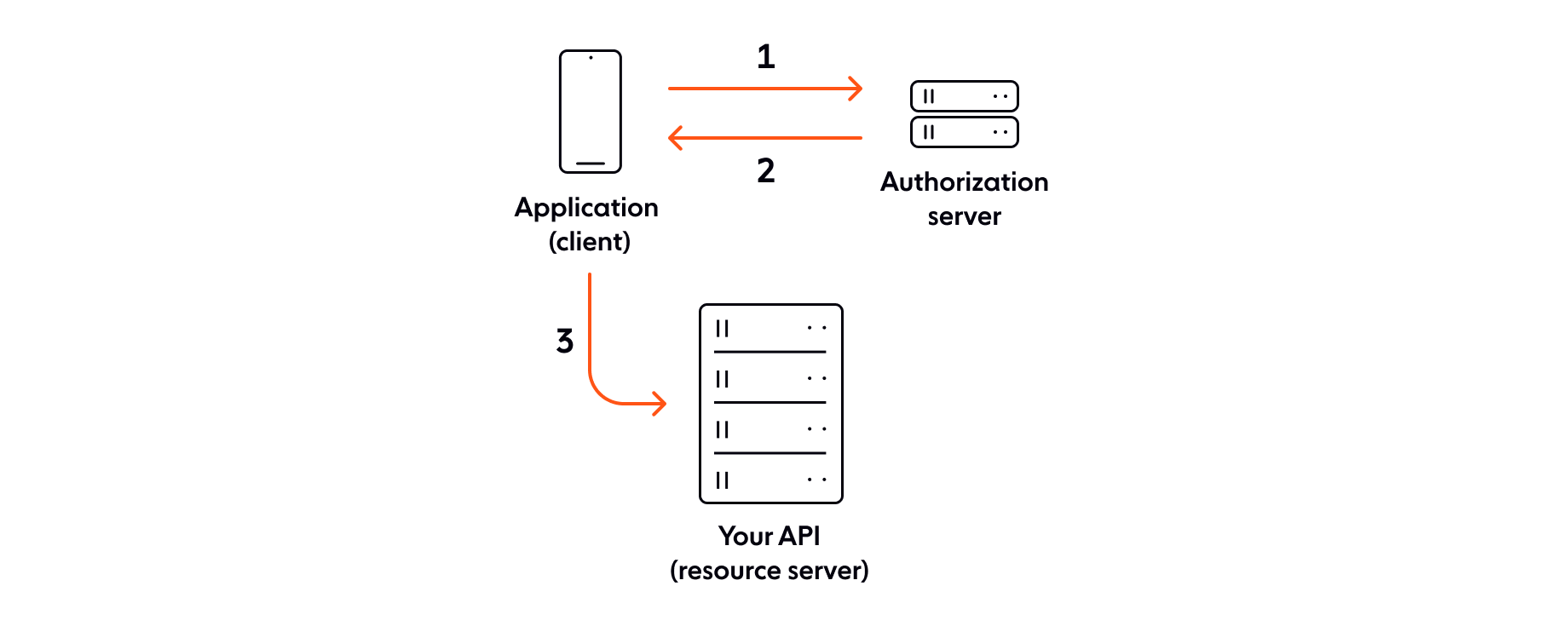
The client sends an authorization request to the authorization server.
The authorization server returns an access token to the client.
The client uses the access token to access a protected resource.
JWT is the recommended strategy on the client-side as it provides more fine-grained access control than basic authentication and limits the risk of exposed or compromised credentials. Furthermore, in addition to JWTs being ephemeral by design, they can also be revoked.
While JWTs are obviously more reliable and secure than basic authentication, they come with some engineering challenges that you will have to manage if you decide to develop your own JWT-based authentication solution:
How do you handle token privileges and permissions?
How do you set TTL (Time To Live)?
How do you renew tokens?
How are tokens sent? If it’s via URL, you need a mechanism that allows you to renew tokens when they expire, without starting a new WebSocket connection.
See how Ably handles authentication
Network compatibility and fallback transports
Despite widespread platform support, WebSockets suffer from some networking issues. The main one is proxy traversal. For example, some servers and corporate firewalls block WebSocket connections.
Ports 80 and 443 are the standard ports for web access and they support WebSockets. Note that port 80 is used for insecure connections. With that in mind, it’s recommended to use port 443 for WebSockets whenever possible, because it’s secure, and prevents proxies from inspecting the connections. If you have to (or wish to) run WebSockets on different ports, network configuration is usually needed.
That said, if you can’t use port 443 and you foresee clients connecting from within corporate firewalls or otherwise tricky sources, you might need to support fallback transports such as XHR streaming, XHR polling, or JSONP polling. That’s why you need to use a client-side WebSocket-based solution that supports fallbacks. This solution can take various forms; you can opt for an open-source library designed specifically to provide lots of fallback capabilities, such as SockJS.
Alternatively, you can build your own complex fallback capability, but the scenarios where you actually have to are very rare. Developing a custom solution is a complex process that takes a lot of time and effort. In most cases, to keep engineering complexity to a minimum, you are better off using an existing WebSocket-based solution that provides fallback options.
Ably’s WebSocket-based protocol
Device power management and heartbeats
By its very nature, a WebSocket connection is persistent. Which also means it’s consuming battery life for as long as it’s active. With WebSockets enjoying support across various development platforms, programming languages, and operating systems, including tvOS, device power management is something essential to consider. Unfortunately, it’s not handled by many WebSocket libraries that support tvOS.
There are several ways you can approach battery management and heartbeats. The WebSocket protocol natively supports control frames known as Ping and Pong. This is an application-level heartbeat mechanism that allows you to detect whether a WebSocket connection is alive. Usually, the server-side sends a Ping frame and, on receipt, the client-side sends a Pong frame back to the server.
You could theoretically also use protocol-level heartbeats — TCP keepalives. However, this is a less than ideal option, as TCP keepalives don’t get passed web proxies. In other words, with TCP keepalives, you can’t always verify a connection end-to-end.
Be aware that the more heartbeats you send, the faster battery is depleted. This can be quite problematic, especially when mobile devices are involved. In these scenarios, to preserve battery life, you may want to use OS-native push notifications where possible. With this approach, there’s no need to maintain a WebSocket connection active, because the server can wake up an inactive instance of your app whenever you send a push notification.
While push notifications are a great choice for waking up an app, they are not a replacement for a WebSocket or streaming protocol layer, because they do not provide quality of service guarantees. Push notifications are typically ephemeral, have variable latencies, and aren’t ordered. Furthermore, there is usually a limited number of push notifications that can be queued up for delivery at any given moment.
Before deciding whether to use heartbeats, push notifications, or both, you must carefully analyze your system requirements and use cases. For example, if you’re developing a chat solution or a multiplayer game, you want to send frequent heartbeats, even if that means battery life is depleted faster. On the other hand, if you are developing an online shop and want to infrequently notify customers about new products, you might want to use push notifications for this specific purpose. Push notifications will better preserve battery life, even if it means that your connection status detection will not be as accurate.
Ably, heartbeats and push notifications
Handling reconnections with continuity
It’s common for devices to experience changing network conditions. Devices might switch from a mobile data network to a Wi-Fi network, go through a tunnel, or perhaps experience intermittent network issues. Abrupt disconnection scenarios like these require a WebSocket connection to be re-established.
For some realtime use cases, resuming a stream after disruption precisely where it left off is essential. Think about features like live chat, where missing messages during disconnection cause confusion and frustration. You need to ensure that your client-side WebSocket implementation is equipped to handle complexities around reconnections. The implementation should also provide the means to resume a stream and offer exactly-once delivery guarantees.
If resuming a stream exactly where it left off after brief disconnections is important to your use case, you need to implement history / persisted data. Getting into the detail of this is out of the scope of this article (see this blog post for more), but these are some things you’ll need to consider:
Caching messages in front-end memory. How many messages do you store and for how long?
Moving data to persistent storage. Do you need to move data to disk? If so, how long do you store it for? Where do you store it? And how will clients access that data when they reconnect?
Resuming a stream. When a client reconnects, how do you know which stream to resume and where exactly to resume it from? Do you need to use a connection ID to establish where a connection broke off? Who needs to keep track of the connection breaking down - the client, or the server?
Backoff mechanism. What is your incremental backoff strategy? How do you prevent your servers from being overloaded in scenarios where you have a high number of clients that keep trying (and failing) to reestablish a connection?
You might even consider whether WebSockets is what you truly need. If your use case doesn’t require bidirectional messaging, but subscribe-only, then a protocol like SSE with stream resume baked in might be a better choice.
See how Ably handles reconnections with continuity
Final thoughts
Hopefully this article has shown you what to expect when implementing a client-side WebSocket-based solution for tvOS. Raw WebSockets will rarely be enough, even for simple use cases. If you want to scale your system and provide optimum experiences for end-users, you will most likely have to use a feature-rich WebSocket solution.
At Ably, we’ve developed an enterprise-ready pub/sub messaging platform that makes it easy to efficiently design, quickly ship, and seamlessly scale critical realtime functionality delivered directly to end-users. We have also developed our very own WebSocket-based protocol, but we also support raw WebSockets, and other protocols, like SSE or MQTT.
Our platform is designed in a manner that enables tvOS developers to offload hard engineering and infrastructure problems to Ably, so they can focus entirely on building their products. That’s why we offer 25+ client-side SDKs, tvOS included.
If you want to talk more about WebSockets or if you’d like to find out more about Ably and how we can help you in your tvOS and WebSockets journey, get in touch or sign up for a free account.
We’ve written a lot over the years about realtime messaging and topics such as WebSockets. Here are some useful links, for further exploration:
Recommended Articles

Building realtime apps with Flutter and WebSockets: client-side considerations
Learn about the many challenges of implementing a dependable client-side WebSocket solution for Flutter apps.

Realtime apps with React Native and WebSockets: client-side challenges
Learn about the many challenges of implementing a dependable client-side WebSocket solution for React Native.
Comparing Socket.IO and HTTP: Key differences and use cases
Discover the different features, performance characteristics and use cases for Socket.io - a realtime library, and the HTTP protocol in our comparison guide.
